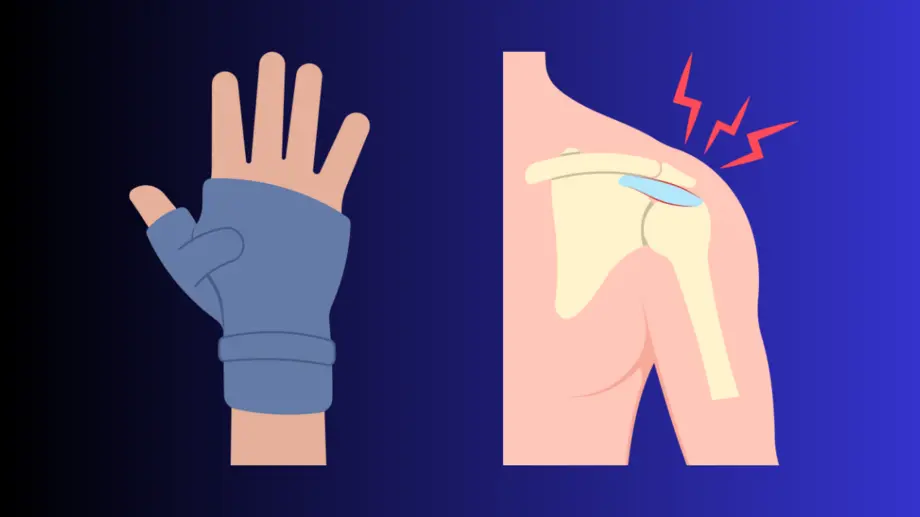
Introduction: RSI Repetitive Strain Injury
Do you feel pain in your wrist after using the computer? Do you feel pain in your shoulder after carrying objects? Do you feel pain in your knee after a run? Then you may have a Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI). Here in this post you’ll find valuable tips for taking better care of your body and preventing injuries.
The concept of RSI
Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI) or Stress Injury are injuries that occur when too much physical effort is placed on a part of the body, resulting in inflammation (pain and swelling), muscle strain or tissue damage. This stress usually occurs after repeating the same movements many times, overloading a region of the body.
RSI at Work (WMSD)
RSIs are quite common work-related injuries, in which case they are called WMSDs (Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders). They are very common among people who spend a lot of time using computers, for example.
RSI in Adolescents
Although more common in adults, RSIs are becoming more frequent in teenagers because they spend so much time using computers, notebooks, cell phones and tablets.
Teenagers who spend a lot of time playing musical instruments or video games are also prone to Repetitive Strain Injury (RSI).
In adolescents, repetitive strain injuries occur more frequently in bone growth plates.
What causes RSI?
Most RSI conditions found are linked to the stress of repetitive movements at the computer or when playing sports. When stress occurs repeatedly over time, the body’s joints don’t have a chance to recover, irritating and inflaming the joints, tendons and muscles.
Some jobs that involve repetitive tasks – such as supermarket cashiers or waiters who spend a lot of time carrying heavy trays – can lead to Repetitive Strain Injury. Playing musical instruments can cause problems with overuse of certain hand or arm movements. Any kind of repetitive movement can cause an injury, including text messaging on cell phones.
RSI in Sport
The use of unsuitable equipment during sports practice is another important factor that can lead to RSI. For example, running in athletic shoes that don’t provide correct support for the feet and ankles is a problem.
The areas most affected by RSIs are the elbows, shoulders, knees and heels.
Symptoms of Repetitive Strain Injury
Symptoms of RSIs include:
- Tingling, numbness or pain in the affected area
- Stiffness or pain in the neck or back
- Feeling of weakness or fatigue in the hands or arms
If you see any of these warning signs of RSI or WMSD, it’s time to see a doctor. Don’t ignore the symptoms or they could lead to more serious problems.
If left untreated, RSIs can become more severe and prevent you from doing simple daily tasks and participating in sports, music and other activities.
Types of Repetitive Strain Injury
Bursitis
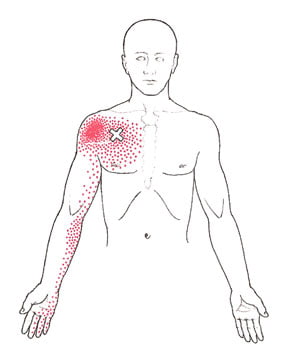 It is the inflammation of a bursa, which is a fluid-filled sac that acts as a kind of cushion for a joint. Signs of bursitis include pain and swelling. It is associated with frequent overloads, carrying heavy backpacks and overuse of certain joints during sports, such as the knee or shoulder.
It is the inflammation of a bursa, which is a fluid-filled sac that acts as a kind of cushion for a joint. Signs of bursitis include pain and swelling. It is associated with frequent overloads, carrying heavy backpacks and overuse of certain joints during sports, such as the knee or shoulder.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome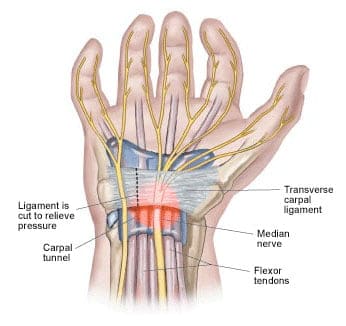
In carpal tunnel syndrome, swelling occurs inside a narrow “tunnel” formed by bone and ligament in the wrist. This tunnel surrounds the nerves that conduct nerve and motor impulses related to the hand, causing pain, tingling, numbness and weakness. Carpal tunnel syndrome is caused by repetitive movements that can happen during activities such as typing or playing video games (using joysticks). It is rare in teenagers and more common in adults, especially those in computer-related jobs.
Epicondylitis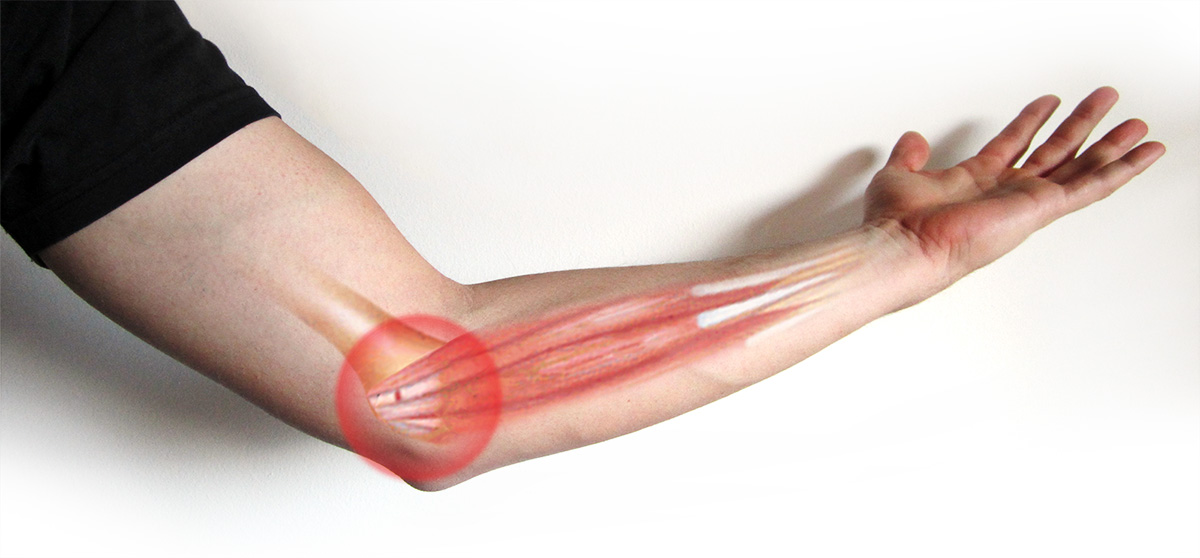
This condition is characterized by pain and swelling at the point where the bones join at the elbow. Epicondylitis is known as “tennis elbow” because it is very common in tennis players.
Osgood-Schlatter disease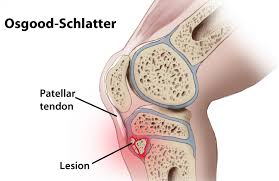
It’s a common cause of knee pain, especially in teenage athletes who are going through a growth phase. Frequent physical stress (such as running long distances) can cause inflammation in the area where the patellar tendon attaches to the backbone.
Paletofemoral syndrome
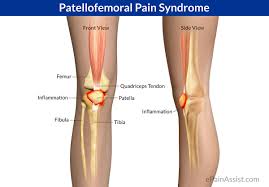 Patellofemoral syndrome affects the cartilage of the patella. Squatting, kneeling or climbing stairs and hills can aggravate pain in the knee area.
Patellofemoral syndrome affects the cartilage of the patella. Squatting, kneeling or climbing stairs and hills can aggravate pain in the knee area.
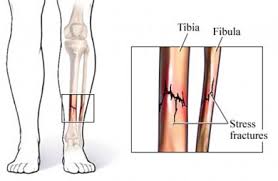
Stress fractures
Stress fractures are small cracks in the surface of the bone caused by repetitive overload. These injuries can occur when a bone is under repeated stress from running, marching, walking, or jumping, or from stress on the body such as when a person runs or walks on an uneven surface or wears worn-out sneakers.
Tendonitis
In tendonitis, inflammation occurs in the tendons. Tendonitis is associated with repetitive overstrain of the tendons due to overuse of certain muscles.
Prevention: how to prevent RSI?
To avoid a Repetitive Strain Injury or RSI when using the computer, make sure that your computer desk allows you to sit and type in a correct position. To find out more about this topic, read our article The main postural vices: the best posture for working, studying and sleeping.
Here are some simple tips to prevent RSIs:
- Make sure that the top of the computer screen is aligned with your forehead.
- Sit up straight with your spine aligned.
- Avoid tensing your shoulders, which can put unnecessary stress on your neck, back and spine.
- Sit with the soles of your feet flat on the floor or on a footrest. (To test whether your legs are in a good position, try placing a pencil on your knee – the pencil should roll towards your waist.)
- The keyboard should be close to you so that you don’t have to stretch or raise your arms too much to reach it.
- Your fingers and wrists should remain aligned when typing. Try a wrist rest for extra support. Your wrists and forearms should be at a 90 degree angle to your arms. Elbows should be placed close to the side of the body.
- Take breaks to stretch or walk every 30 minutes – even if you don’t feel tired or have any pain.
- Gymnastics is also an important ally in preventing RSIs.
Sports Injury Prevention
- Stretch properly before and after practicing sports.
- Wear the appropriate clothing and equipment for your sport.
- Stay well hydrated during and after exercise. Listen to your body and rest when you feel tired.
- If you are experiencing symptoms such as pain, swelling, numbness or stiffness during your sport, stop playing immediately and consult your doctor as soon as possible.
The Treatment of Stress Injury (RSI)
 The sooner RSI is diagnosed, the sooner you can be cured, so make sure you see your doctor,
The sooner RSI is diagnosed, the sooner you can be cured, so make sure you see your doctor,
The doctor will try to assess how the injury occurred and which movements cause pain. Your doctor may carry out X-rays, blood tests or other tests to make sure there are no other health problems.
If you are diagnosed with RSI or WMSD, resting the affected area is the best way to get better. Your doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory medication (such as ibuprofen) for a period of time. The use of ice (cold compress) is recommended to reduce swelling and pain.
After the pain and swelling have gone, physiotherapy treatment is recommended.
Did you like this post? Share it and leave your review below. Didn’t like it? Did you find any mistakes? Leave a comment because we always want to improve.
Source: Federal Council of Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy – COFFITO
Video: RSI or WMSD